In this post, I’ll implement a post deployment check that waits until the application is running with the expected version. The first step is to make the application aware of its version. The easiest way to do that in our setup is with an environment variable. We’ll modify the deployment template of the Helm chart:
env:
- name: APP_VERSION
value: {{ .Values.image.tag }}
The .Values.image.tag is already set to the correct version during deployment, so we get this for free.
The second step is to expose this version information from the application. We’ll create a new endpoint, /version, which will simply print this version information:
app.get('/version', (req, res) => res.send(process.env.APP_VERSION));
At this point, our application is able to print its version. We’ll use this endpoint in a script. The script, wait-for-version.sh, will poll this endpoint until it prints the expected version:
#!/bin/bash
#
# Wait until the version endpoint reports the expected version.
# Usage: wait-for-version.sh version-url expected-version
# Example: wait-for-version.sh http://some.host/version 1.3.0
set -e
VERSION_URL=$1
if [ -z "$VERSION_URL" ]; then
>&2 echo "ERROR: first parameter should be version URL."
exit 1
fi
EXPECTED_VERSION=$2
if [ -z "$EXPECTED_VERSION" ]; then
>&2 echo "ERROR: second parameter should be the expected version."
exit 1
fi
# how many times to retry
RETRY_COUNT=${RETRY_COUNT:-12}
# how many seconds to wait between retries
SLEEP_TIME=${SLEEP_TIME:-5}
n=0
until [ $n -ge $RETRY_COUNT ]
do
echo "Waiting for url $VERSION_URL to be at version $EXPECTED_VERSION, attempt $n..."
ACTUAL_VERSION=$(curl $VERSION_URL)
if [ "$EXPECTED_VERSION" = "$ACTUAL_VERSION" ]; then
echo "Version is correct!"
exit 0
fi
echo "Version was $ACTUAL_VERSION"
n=$[$n+1]
sleep $SLEEP_TIME
done
>&2 echo "ERROR: expected version did not appear in time."
exit 1
To use this script, we’ll add a new step in the deploy template which uses it. First, we’ll setup a few parameters in the template:
app.host: the host name e.g.test.blog-helm.localfor the test environment.app.baseurl: the base URL e.g.http://test.blog-helm.localapp.version.url: the URL the script should use to get the application's version, e.g.http://test.blog-helm.local/version
Note that the only parameter we need to specify in the deployment build configurations is the app.host; the others can be calculated based on that:

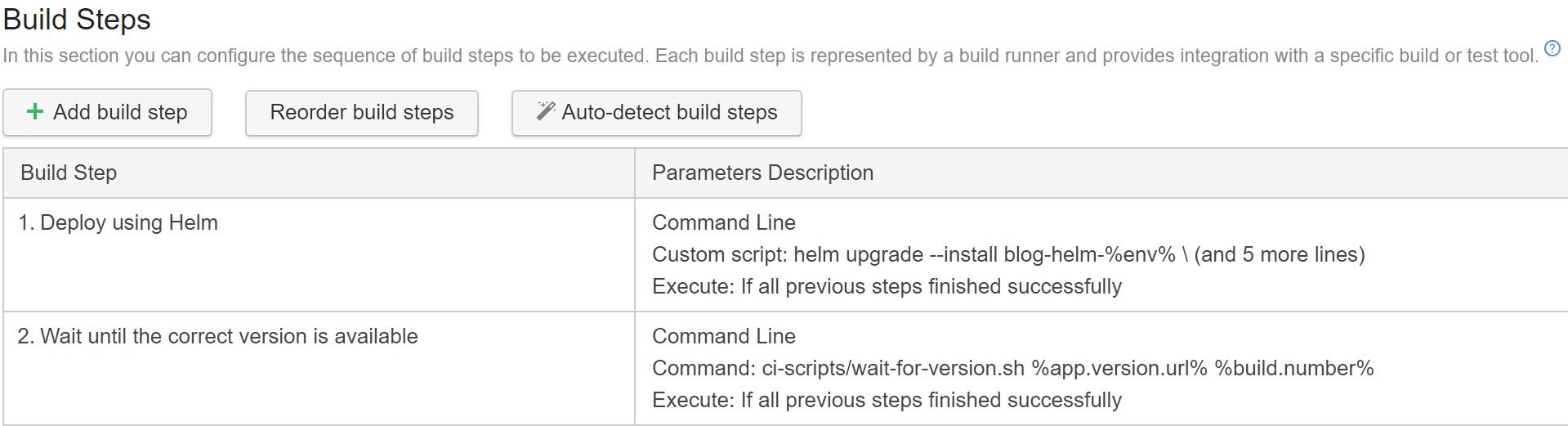
The build step is simply running the wait-for-version script, with parameters %app.version.url% and %build.number%:
Here’s an example of the output log:
[09:55:39][Step 2/2] Waiting for url http://test.blog-helm.local/version to be at version 1.7.1, attempt 0...
[09:55:39][Step 2/2] Version was 1.7.0
[09:55:44][Step 2/2] Waiting for url http://test.blog-helm.local/version to be at version 1.7.1, attempt 1...
[09:55:44][Step 2/2] Version was <html>
[09:55:44][Step 2/2] <head><title>503 Service Temporarily Unavailable</title></head>
[09:55:44][Step 2/2] <body bgcolor="white">
[09:55:44][Step 2/2] <center><h1>503 Service Temporarily Unavailable</h1></center>
[09:55:44][Step 2/2] <hr><center>nginx/1.13.6</center>
[09:55:44][Step 2/2] </body>
[09:55:44][Step 2/2] </html>
[09:55:49][Step 2/2] Waiting for url http://test.blog-helm.local/version to be at version 1.7.1, attempt 2...
[09:55:49][Step 2/2] Version is correct!
As you can see, initially the version was old (1.7.0 instead of the expected 1.7.1). Then, the app returned 503 as it was being deployed. Finally, the correct version was activated, so the script succeeded.